One of the best things about an RV is the self-contained power system that allows us to have all the comforts without being plugged into an electric outlet. This 12 volt system can be a joy or a headache, depending on how you maintain and utilize it. If you ignore basic maintenance, it'll let you down at the worst possible time! An understanding of the components and principles involved is necessary to get the most out of your 12 volt system. Relax, tho... it's not "rocket science"!.... your 12 volt system is simple and very easy to understand and maintain. Let's just take a look at a block diagram of a typical RV 12 volt system.
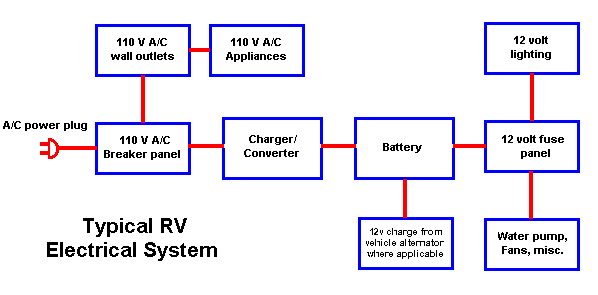
As you read through this information, we will talk about all the different
parts of this system and discuss some of the very useful additions and
improvements that you can make yourself. Also included will be some highly
technical info that you can bypass if it doesn't interest you. So, let's get
started by talking about batteries. The battery is the heart of the 12 volt
system. No other single component is as critical to the system's functioning
as your battery system! That's why a lot of time needs to be spent talking
about the care and feeding of your battery(s).
Sure, we all know what a battery is.... it's that thing that goes dead when you leave the headlights on overnight! Actually, there's a little more to it than that, so perhaps a review of battery basics is in order here..
A battery is an electrical storage device. Batteries do not make electricity, they store it, just as a water tank stores water for future use. As chemicals in the battery change, electrical energy is stored or released. In rechargeable batteries this process can be repeated many times. Batteries are not 100% efficient - some energy is lost as heat and chemical reactions when charging and discharging. If you use 1000 watts from a battery, it might take 1200 watts or more to fully recharge it. Slower charging and discharging rates are more efficient. Practically all batteries used in RV applications are Lead-Acid type batteries. Even after over a century of use, they still offer the best price to power ratio.
Batteries are divided in two ways, by application (what they are used for) and construction (how they are built). The major applications are automotive, marine, and deep-cycle. Deep-cycle includes solar electric (PV), backup power, and RV and boat "house" batteries. The major construction types are flooded (wet), gelled, and AGM (absorbed glass mat). AGM batteries are also sometimes called "starved electrolyte", because the fiberglass mat is only 90% saturated with Sulfuric acid. Flooded may be standard, with removable caps, or the so-called "maintenance free" (without caps). All gelled are sealed and a few are "valve regulated", which means that a small valve keeps a slight positive pressure in each cell. Most AGM batteries are sealed and valve regulated. Sealed gell and AGM batteries offer the convenience of no maintenance and produce less gas, so at first glance, they may appear more attractive than standard flooded cell batteries. There is a down side here, tho.... These batteries, especially the gell cell type, require precise control of the charging process to prevent permanent damage by overcharging. They also tend to be significantly more expensive and have a somewhat shorter lifespan. It all depends on what premium you put on the maintenance free aspect of it. In my opinion, the standard flooded cell battery offers better overall performance for the price and will probably last a lot longer in most common RV applications. The need to add water periodically is a small price to pay for the advantages you get. I strongly suggest that you avoid the "maintenance free" flooded cell batteries... they truly aren't a good design: they are simply a standard flooded cell battery with sealed cells. Each cell has a small valve to release excessive pressure. They still can be run low on electrolyte with heavy usage and fast charging, and there's no way to add water, so the batteries often die young.
It's important to understand the differences in battery types...
Starting batteries are normally used to start and run engines. Engine starters need a very large starting current for a very short time. Starting batteries have a large number of thin plates for maximum surface area. The plates are composed of a Lead "sponge", similar in appearance to a very fine foam sponge. This gives a very large surface area, but if deep cycled, this sponge will quickly be damaged and will fall to the bottom of the cells. Automotive batteries will generally fail after 30 or more deep cycles.
Deep cycle batteries are designed to be discharged down as much as 80% repeatedly, and have much thicker plates. The major difference between a true deep cycle battery and others is that the plates are solid Lead plates - not sponge. Unfortunately, it is often impossible to tell what kind of battery you are really buying in some of the discount stores or places that specialize in automotive batteries.
Many Marine batteries are actually "hybrid", and fall between the starting and deep-cycle batteries, while a few are true deep cycle. In the hybrid, the plates may be composed of Lead sponge, but it is coarser and heavier than that used in starting batteries. It is often hard to tell what you are getting in a "marine" battery, but most are a hybrid. "Hybrid" types should not be discharged more than 50%.
A battery's capacity for storing energy is rated in several different ways, depending on the battery type. Starting batteries are often rated in Cold Cranking Amps or CCA. CCA is the discharge load in amps which a battery can sustain for 30 seconds at 0 degrees F. and not fall below 1.2 volts per cell (7.2V on 12V battery). This battery rating measures a burst of energy that a car needs to start on a cold morning.
Deep cycle batteries are often rated in Amp/Hours. Amp/Hour rating of battery capacity is calculated by multiplying the current (in amperes) by time (in hours) the current is drawn. For example: A battery which can deliver 4 amperes for 20 hours before being discharged would have a 80 amp-hour battery rating (4 X 20= 80).
You may also see batteries rated with a Reserve Capacity. RC is the number of minutes a new, fully charged battery at 80 degrees F. will sustain a discharge load of 25 amps to a cut-off voltage of 1.75 volts per cell (10.5V on 12V battery). This battery rating measures more of a continuous load on the battery. For RV use, this rating is a little less useful, as the common loads that RV use puts on a battery are a lot less than that 25 amp load used to determine RC.
I feel that the best bet is to consider batteries by their amp/hour rating,
so that is the rating method used throughout this article.
Now that we know a little more about batteries, it becomes obvious what we should be using in the RV. Deep cycle batteries! When you unplug from the A/C line and go boondocking for a weekend, you are using only your batteries to provide power for your rig. It's not uncommon for those batteries to be fairly well discharged before you get back to civilization and plug in. Starting batteries and "Marine" batteries just aren't designed for this kind of use and will die an early death in your RV. Use only deep cycle batteries! This is so simple that you'd think it would be a no-brainer, but a lot of RVs (especially used ones!) leave the dealer's lot with starting or Marine type batteries installed. If you recently bought your rig, it may be worthwhile to check and see just what batteries you actually have installed.
Selecting the correct batteries is all about lifespan.... The right
batteries will last a lot longer, leaving you with more money for the finer
things in life! The lifespan of a battery will vary considerably with how it
is used, how it is maintained and charged, temperature, and other factors.
We'll talk more about maximizing the lifespan of your batteries later, but for
now, here are some typical expectations for batteries used in deep cycle
service:
Starting: 3-12 months
Marine: 1-6
years
Golf
cart: 2-8 years
Deep cycle
(L-16 type etc.): 4-8 years
- AGM deep cycle: 4-10 years
Gelled deep cycle: 2-5 years
There are a lot of different battery sizes out there... here are some common battery size codes and approximate sizes and ratings:
|
|
( L x W x H) |
|
|
|
| Group 24 | 10.87 X 6.58 X 9.97 | 53 lb. | 70-85 Amp hours | 12 volts |
| Group 27 | 12.60 X 6.60 X 9.97 | 63 lb. | 85-105 Amp hours | 12 volts |
| Group 31 | 12.94 X 6.74 X 9.88 | 68 lb. | 95-125 Amp hours | 12 volts |
| 4-D | 20.73 X 8.66 X 10.27 | 130 lb. | 180-215 Amp hours | 12 volts |
| 8-D | 20.62 X 10.95 X 10.17 | 158 lb. | 225-255 Amp hours | 12 volts |
| Golf cart & T-105 | 10.37 X 7.13 X 11.57 | 61 lb. | 180 to 220 Amp hours | 6 volts |
| L-16 | 11.69 X 7.13 X 16.69 | 114 lb. | 340 to 380 Amp hours | 6 volts |
A lot of RVers have switched from the "standard" group 24 or 27 12 volt batteries to the larger 6 volt golf cart batteries. If you have room for at least 2 of them, they are a good choice. They are true deep cycle batteries and will last a lot longer than most common 12 volt batteries in your RV. They are physically larger, so you must measure carefully before buying them, but I recommend you use them if you can. I have a set of Trojan Golf cart batteries that are going on 5 years old and they still have almost all of their original capacity. They are priced about the same as (or a bit lower than) the common 12 volt deep cycle battery. Golf cart batteries have a higher capacity than group 24 and 27 batteries... a pair of group 24 12 volt batteries only provide 140-170 amp/hours of capacity, where a pair of golf cart batteries provide 180-220 amp/hours. There are other deep cycle batteries available, such as the L-16 and AGM types, that are extensively used in large solar and alternate energy systems, but their physical size and added expense make them a less attractive choice for the average RVer.
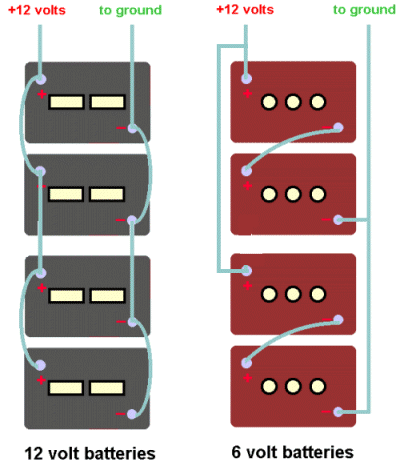
If you have room and want to change over to the 6 volt golf cart batteries, you must make an important wiring change. Most rigs that have 2 or more 12 volt batteries have them wired in parallel. when going to the 6 volters, you must wire pairs of them in series to produce the needed 12 volts. This is actually simpler than it sounds.... see the diagrams below.
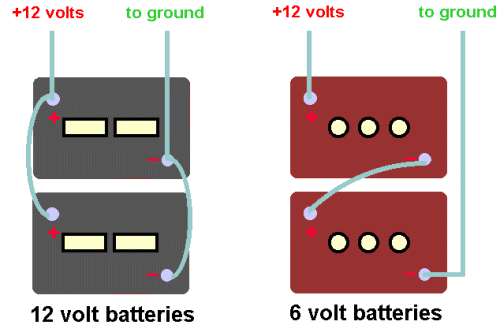
When installing new batteries, first mark the cables so you do not forget which one is which when you reconnect. If you are changing over from a pair or set of 12 volt batteries to a pair or set of 6 volt batteries, some changes in cabling will be required. See the wiring drawing above for an example.. If you don't fully understand what the difference is between parallel and series wiring, I strongly suggest that you do not attempt to do the hookup yourself... get a competent RV mechanic to show you how. If you are building a bigger battery bank, see below for wiring info...
When replacing your batteries, remove the negative cable first because this will minimize the possibility of shorting the battery when you remove the other cable. Next remove the positive cable and then the hold-down bracket or clamp. If the hold down bracket is severely corroded, replace it. Dispose the old battery by exchanging it when you buy your new one or by taking it to a recycling center. Please remember that batteries contain large amounts of harmful lead and acid.
After removing the old battery(s), be sure that the battery tray and cable terminals or connectors are clean. Auto parts stores sell a cheap wire brush that will allow you to clean the inside of a terminal clamps and the terminals. If the terminals, cables or hold down brackets are severely corroded, replace them. Keep track of the markings you made on the cables before replacing them!
Thinly coat the terminals and terminal clamps with a high temperature grease or petroleum jelly (Vaseline) to prevent corrosion. Place the replacement battery(s) so that the cables will connect to the correct terminals. Be extra careful here, as reversing the polarity of the battery when connecting it may severely damage or destroy some parts of your RV electrical system. Replace the hold-down brackets or straps to secure the batteries in place, then reconnect the cables in reverse order, i.e., attach the positive cable first and then the negative cable last.
Before using the battery(s), check the electrolyte levels and state-of-charge. Refill or recharge as required.
A word of Caution:
If you have decided to add additional batteries to your rig, be sure to
either use the existing battery compartment or a compartment specially
designed and vented for batteries. Never place batteries in an unvented
compartment as potentially explosive hydrogen gas will build up. Never place
batteries in any compartment where electrical sparks or other ignition
sources may exist. ( a simple 12 volt light with a switch on it is an
excellent source of ignition spark!!) Notice that the existing battery
compartment on your rig is (or, at least, it should be!!) isolated from all
other areas of the rig and possible ignition sources. Also, be sure to
secure batteries with straps or brackets to prevent movement when the rig is
in motion. An unsecured battery may tip over and spill acid, or worse, may
short out against the rig frame or other metal objects and cause a fire. If
you are setting up a new battery bank in your rig, don't do a half-assed
job!
Now that you have made the choice of what kind of batteries you will use, and have successfully installed them in your rig, it's time to talk about maintenance. In order to get the most from your new batteries, you can't just forget them now and expect them to work for you forever. It is very important to take good care of your new batteries and treat them right.
You must keep an eye on the electrolyte level in the batteries. Most premature failures are caused by low electrolyte levels, and there's just no excuse for it, as it's simple and cheap to keep the batteries filled to the top. Electrolyte is lost whenever the batteries are charged and also when the batteries are discharged heavily. You should check the level in each cell of your batteries regularly. I recommend at least once a month, but it may be necessary to check and top off your batteries more often, depending on usage and how you charge them. At all costs, you must keep the electrolyte level above the plates at all times. In the warmer climates and during the summer, check the electrolyte levels more frequently. To replenish the electrolyte, add distilled water as required. Never add acid-- just distilled water and do not overfill. Never use anything except distilled water! Tap water contains a lot of chemical and mineral impurities and will kill your battery before it's time.
A word of Caution: Batteries contain a sulfuric acid electrolyte which is a highly corrosive liquid. Don't get any on you! In case of a spill or splash, immediately flush the affected area with lots of cold water to dilute the acid. A mixture of baking soda and water can also be used to neutralize the acid, but watch out for the foam that will be generated! Be careful and pay attention to what you are doing! Also, avoid generating sparks, smoking or open flames in the vicinity of batteries.... batteries produce flammable hydrogen gas (remember the Hindenburg?) and can explode violently if the gas is ignited. This is especially important when batteries are housed inside any sort of compartment. Again, protective clothing and safety glasses are recommended to protect you in case of accident. Please treat batteries with the respect they deserve.
Maintaining the correct electrolyte levels, tightening loose hold-down clamps and terminals, and removing corrosion is normally the only preventative maintenance required for a battery. However, you can extend your battery's life by keeping your battery charged properly and avoid deep discharges. Let me explain:
A battery "cycle" is one complete discharge and recharge cycle. It is usually considered to be discharging from 100% to some point not lower than 20%, and then charging back up to 100%. Battery life is directly related to how deep the battery is cycled each time. If a battery is discharged to only 50% each cycle, it will last about twice as long as if it is cycled to 20%. Running the battery down totally flat will have a very negative effect on the lifespan of the battery. See the table below for voltages as related to depth of discharge. This chart is designed to be used when monitoring a battery under load. This chart is a little more useful to the average RVer, as we are most interested in monitoring the state of charge of our battery bank while it is actually in use. See the Testing your batteries section below for information on determining open circuit state of charge using either a volt meter or a specific gravity tester.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If the battery has been charging, then it's important to let the battery set for 2 to 3 hours without a load or charger connected to stabilize before testing. Otherwise, your reading will be high, caused by a phenomenon called "surface charge" It is also necessary to invest in a good digital voltmeter.... it's the only meter that will offer the necessary accuracy to properly test your battery system. That little analog gauge that is part of your RV monitor panel is not very accurate or useful. It's possible to install your own panel mount digital voltmeter... I'll tell you more about that in the section on monitoring. For now, it's important that you understand that your battery's life is adversely affected by too deep a discharge.
At this point, it's also important to note that the battery voltage will be affected by temperature.... The chart above, and most other ratings applied to Lead/Acid batteries assume that the battery is at room temperature: 21 degrees C or about 70 degrees F. As the temperature of the battery drops, so will the fully-charged voltage reading. I have found a lot of conflicting information about this phenomenon, but it seems to be safe to say that for each 10 degrees F drop in temp, you can expect to see the voltage drop about a tenth of a volt. (.10 volt) That means that a battery at 32 degrees F with a no-load voltage reading of 12.35 volts is fully charged.
Battery capacity (how many amp-hours it can hold) is reduced as temperature goes down, and increased as temperature goes up. This is why your car battery dies on a cold winter morning, even though it worked fine the previous afternoon. At freezing, the battery's capacity is reduced by 20%. At approximately -22 degrees F (-27 C), battery AH capacity drops to 50%. Capacity is increased at higher temperatures - at 122 degrees F, battery capacity would be about 12% higher. Even though battery capacity at high temperatures is higher, battery life is shortened. Battery capacity is reduced by 50% at -22 degrees F - but battery LIFE increases by about 60%. Battery life is reduced at higher temperatures - for every 15 degrees F over 77, battery life is cut in half. In reality, this is fascinating information, but isn't really terribly important. Most RVers experience a wide range of temperatures and conditions, so your batteries will average out just fine... I only include this information to give you some feel for the fact that temperature plays a part in battery life and capacity. Don't worry about it!