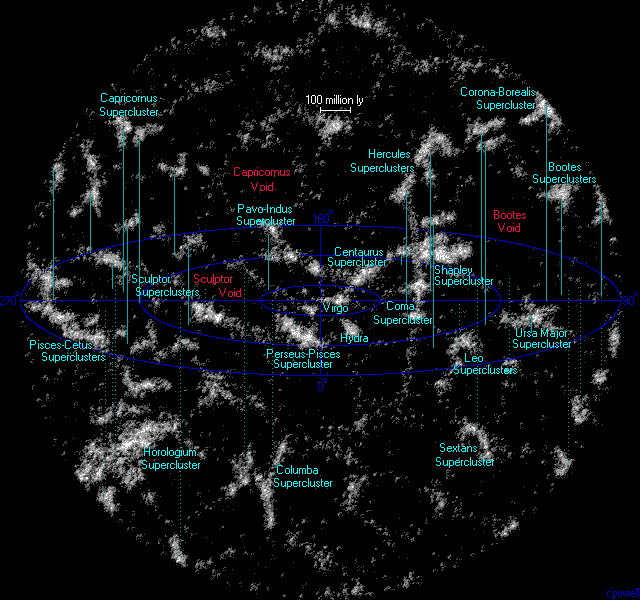
| Hydra Supercluster |
|---|
 |
A nearby supercluster that is very similar in size and shape to the Virgo supercluster.
The Hydra supercluster is also dominated by one rich cluster of galaxies - A1060, one of
the nearest clusters in George Abell's catalog of rich galaxy clusters. |
| Centaurus Supercluster |
|---|
 |
The nearest large supercluster. The Centaurus supercluster is a long supercluster
containing four rich galaxy clusters - A3526, A3565, A3574 and A3581 as well as
hundreds of smaller groups of galaxies. A3526 is the dominant cluster among these and
lies 140 million light years away. Seen from a large distance, the Virgo and Hydra
superclusters might look like appendages to the Centaurus supercluster. The Centaurus
supercluster lies near the Great Attractor - a large collection of matter affecting
the motion of our galaxy and others. It is obscured by the plane of our own galaxy,
but it is probable that the large cluster A3627 is largely responsible. |
| Perseus-Pisces Supercluster |
|---|
 |
A very prominant supercluster. This supercluster is a large sheet of galaxy groups
scattered around three rich clusters - A262, A347 and A426. A426 is very rich cluster
containing thousands of galaxies. |
| Pavo-Indus Supercluster |
|---|
 |
This is a fairly weak supercluster that marks one end of a long wall of galaxies that
encompasses the Centaurus supercluster and probably the Virgo supercluster as well. The
Pavo-Indus supercluster contains three rich galaxy clusters - A3656, A3698 and A3742. |
| Coma Supercluster |
|---|
 |
This is a small but very famous supercluster about 300 million light years away. There
are two very rich galaxy clusters here - A1367 and A1656, both containing thousands of
galaxies. A1656 is a very famous cluster, it is known as the Coma cluster, and as
long ago as 1933 Fritz Zwicky studied the motion of the galaxies in this cluster to
determine the amount of dark matter there is in the Universe. The Coma supercluster
lies at the centre of The Great Wall, a vast filament of galaxies that stretches over
hundreds of millions of light years, one end of which terminates on the Hercules
supercluster. It was the first wall of galaxies recognised, but there are now many
more known. |
| Sculptor Supercluster |
|---|
 |
Two superclusters in the Sculptor and Phoenix regions of the sky mark the position of
a very long wall of thousands of galaxy groups stretching over nearly a billion light
years of space. This is probably the longest of the nearby walls of galaxies. |
| Hercules Supercluster |
|---|
 |
Two famous and prominant superclusters lie here. The smaller and nearer one is
probably the most famous being dominated by two rich clusters - A2197 and A2199 that
lie very close to each other. This supercluster lies 400 million light years away.
The second supercluster is only slightly further - 500 million light years, but it
is a lot bigger and contains lots of rich galaxy clusters scattered around hundreds
of smaller galaxy groups. |
| Leo Supercluster |
|---|
 |
Several large galaxy clusters on the border of Leo and Ursa Major at a distance
of 450 million light years mark the presence of another large supercluster. The
dominant clusters here are A1185 and A1228. |
| Shapley Supercluster |
|---|
 |
This is a very famous supercluster. Although it was only discovered in
1989 it is named after Harlow Shapley who first noticed an excess of galaxies in
part of this region of the sky in the 1930's. The Shapley supercluster is a
massive supercluster and many studies have been carried out on it and although it
is not the biggest supercluster known, it is certainly one of the densest. There
are two main concentrations - one at 500 million light years and a larger one at
650 million light years. There are at least twenty rich galaxy clusters among the
thousands of galaxy groups in this supercluster, including three of the richest
galaxy clusters known: A3558, A3559 and A3560. |
| Pisces-Cetus Supercluster |
|---|
 |
This is a region containing several major superclusters over 800 million light years
away noted by Brent Tully in 1986. There are several very large superclusters here
forming long wall structures hundreds of millions of light years in length. |
| Bootes Supercluster |
|---|
 |
There are a couple of prominant superclusters in Bootes over 800 million light years
away but this region of the sky is more famous for the large Bootes Void that lies
next to them. It is about 300 million light years across. There are no major clusters
of galaxies in this void, but some individual galaxies have been noted, so it is not
completely empty. |
| Horologium Supercluster |
|---|
 |
This is a huge supercluster 900 million light years away. It is not as dense as the
Shapley supercluster but it contains a large number of rich galaxy clusters scattered
across half a billion light years making it one of the largest known superclusters.
This is another region of the sky in which Harlow Shapley noticed an excess of galaxies.
Galaxy surveys in this part of the sky also show that there is a smaller supercluster
lying in front of it 600 million light years away. In astronomy journals the Horologium
supercluster is sometimes called the Horologium-Reticulum supercluster. |
| Corona Borealis Supercluster |
|---|
 |
The most distant of the famous superclusters. It has long been recognised that there
are a large number of rich galaxy clusters in this small constellation. A2065 is
probably the dominant cluster here, but there are another nine or ten large clusters here
which are also rich. The supercluster is about 1 billion light years away. |
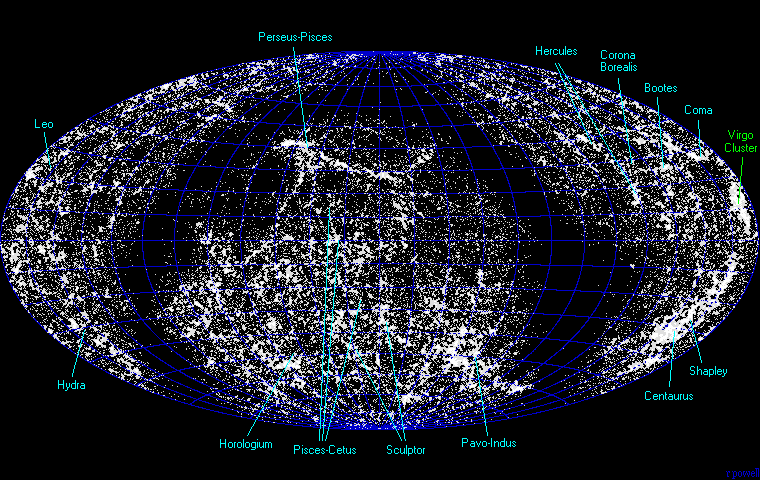
An all-sky plot of the 60000 brightest galaxies shows how galaxies
clump together into large supercluster formations. The positions of some of the major
superclusters are marked although only the nearest superclusters are prominant. Only
four of these galaxies are visible with the naked eye. The large, dark, circular band
is the plane of our own Galaxy where it is difficult to see distant galaxies because of
all the foreground gas, dust and stars.